遗传算法新手教学?(最好有案例,一步一步的分解)
-
 177*****796
2020-03-23 17:39:33
177*****796
2020-03-23 17:39:33
这是本人见过最详细的步骤了:
需要如下主函数:
编码和种群生成
function [pop] = initializega(num,bounds,evalFN,evalOps,options)
% pop - the initial, evaluated, random population
% num - the size of the population, i.e. the number to create
% bounds - the number of permutations in an individual (e.g., number
% of cities in a tsp
% evalFN - the evaluation fn, usually the name of the .m file for evaluation
% evalOps- any options to be passed to the eval function defaults [ ]
% options- options to the initialize function, ie. [eps, float/binary, prec]
% where eps is the epsilon value and the second option is 1 for
% orderOps, prec is the precision of the variables defaults [1e-6 1]
交叉
function [c1,c2] = arithXover(p1,p2,bounds,Ops)
% Arith crossover takes two parents P1,P2 and performs an interpolation
% along the line formed by the two parents.
%
% function [c1,c2] = arithXover(p1,p2,bounds,Ops)
% p1 - the first parent ( [solution string function value] )
% p2 - the second parent ( [solution string function value] )
% bounds - the bounds matrix for the solution space
% Ops - Options matrix for arith crossover [gen #ArithXovers]
选择
normGeomSelect:NormGeomSelect is a ranking selection
function based on the normalized geometric distribution.
(基于正态分布的序列选择函数)
变异
function[newPop] = normGeomSelect(oldPop,options)
% NormGeomSelect is a ranking selection function based on
the normalized
% geometric distribution.
%
% function[newPop] = normGeomSelect(oldPop,options)
% newPop - the new population selected from the oldPop
% oldPop - the current population
% options - options to normGeomSelect
[gen probability_of_selecting_best]
一些辅助函数:
f2b :Return the binary representation of the float number
fval(将浮点数转化为二进制数)
b2f:Return the float number corresponing to the binary
representation of bval. (将二进制数转化为
浮点数)
nonUnifMutation: Non uniform mutation changes one
of the parameters of the parent based on a non-uniform
probability distribution. This Gaussian distribution starts wide,
and narrows to a point distribution as the current generation
approaches the maximum generation.
(基于非均一概率分布进行非均一变异)
maxGenTerm:Returns 1, i.e. terminates the GA when the
maximal_generation is reached.
(当迭代次数大于最大迭代次数时,终止遗传算法,返回
为1,否则返回为0。)
roulette:roulette is the traditional selection function with the
probability of surviving equal to the fittness of i / sum of the
fittness of all individuals
三、应用举例
1.计算下列函数的最大值。
f(x)=x+10*sin(5x)+7cos(4x) , x∈[0,9]
方式1 >>gademo
方式2
step 1 编写目标函数gademo1eval1.m
function [sol, val] = gaDemo1Eval(sol,options)
x=sol(1);
val = x + 10*sin(5*x)+7*cos(4*x);
step 2 生成初始种群,大小为10
initPop=initializega(10,[0, 9],'gademo1eval1',[],[1e-6,1]);
step 3 25次遗传迭代
[x, endPop,bpop,trace] = ga([0 9],'gademo1eval1',[],initPop,...
[1e-6 1 1],'maxGenTerm',25,...
'normGeomSelect',[0.08],...
['arithXover'],[2],...
'nonUnifMutation',[2, 25 ,3])
% Output Arguments:
% x - the best solution found during the course of the
run
% endPop - the final population
% bPop - a trace of the best population
(解的变化)
% traceInfo - a matrix of best and means of the ga
for each generation
(种群平均值的变化)
%
% Input Arguments:
% bounds - a matrix of upper and lower bounds
on the variables
% evalFN - the name of the evaluation .m function
% evalOps
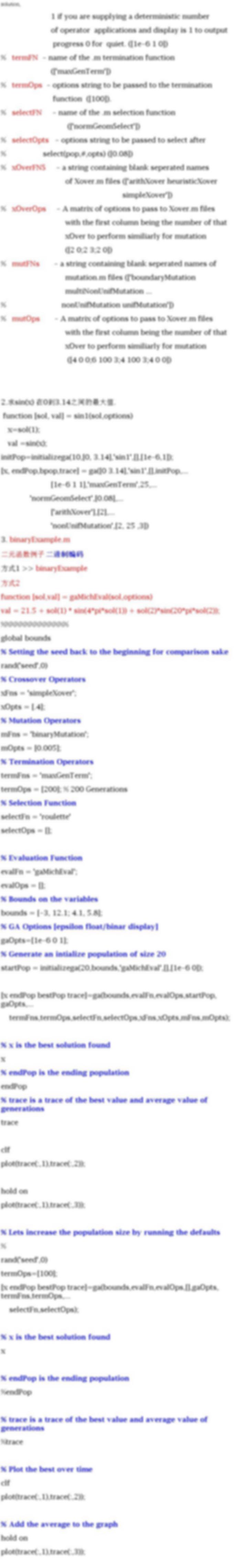
- options to pass to the evaluation function ([NULL])
% startPop - a matrix of solutions that can be initialized
% from initialize.m
% opts - [epsilon, prob_ops ,display]
change required to consider two solutions
different, prob_ops 0 if you want to apply the
% genetic operators probabilisticly to each
 我要购买
我要购买